ELECTRONICS.CA PUBLICATIONS announces the availability of a new report entitled “5G: What Are the Real Status and the Real Economics?”.
5G refers to a set of international standards for a new (5th)
generation of mobile communications service. It is intended to
ultimately replace the service currently available in most of the US –
4G LTE. It is designed to be much faster (maybe up to 100 times as fast
as 4G LTE) in terms of download or upload speeds. Data reception is
anticipated to have much lower latency (time spent in transmission) so
that the data is in very near real-time – close to zero lag. This added
speed is excellent, and it is often a discussion topic, but it is not
the real objective of 5G. The aim is to provide higher capacity on our
mobile networks. Higher capacity for data, for voice, but mostly for
video. Why the need for added traffic capacity? Simple: Cisco is now
estimating that the compound annual growth rate of mobile traffic
through 2022 is 36%! Our 4G-LTE networks are already nearing capacity in
large cities, and yet are facing this impossible growth curve. The 5G
is the answer to provide a vast new ability to meet this growing demand.
All the other rationales for 5G are dreams; this is the driving reason.
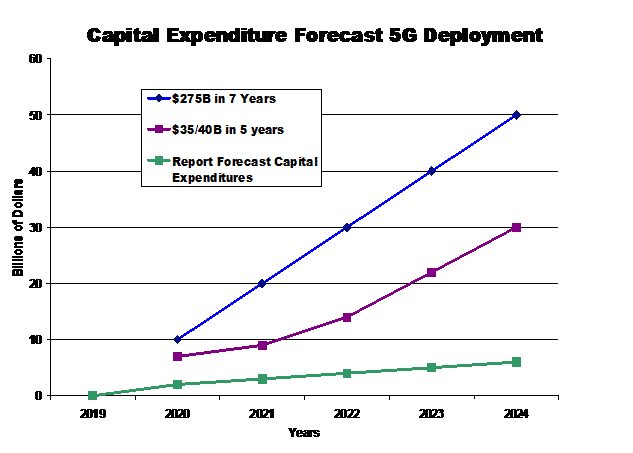
The
first question mostly ignored is the cost. There are many estimates
available for 5G full deployment (small cells, mmWave) in the US. Early
(2017) estimates fell in the $28B to $36B range for five years. Newer
estimates now suggest that the cost over seven years would be as much as
$275B and that the fiber alone needed for deploying the small cells
would be as much as $130B-$150B. For a reference point, $275B would be
well over ten times the total AT&T 2019 Capital Budget! A current
study takes a different approach to the cost question and estimates that
the total cost of ownership (TOC – includes maintenance, capital, and
all fees) could increase for the mobile networks by as much as 300%!

These are big numbers – yes, the B’s above are billions of dollars.
These numbers suggest that we may be letting the technical hype run away
with reality. A sudden conversion to a fully developed 5G large metro
island, as is depicted in the many beautiful drawings, would be
prohibitively expensive without some new services that would help,
substantially, pay the bills. The question is, what new services pay for
this? Alternatively, where are the added customers who pick up this big
tab?
This comprehensive report is going to consider these issues
and ultimately suggest the likely scenario for 5G deployment and
associated five-year expenditures in this country. It moves into a
discussion of 5G from many viewpoints, including objectives, frequency
plans, architecture, and a listing and analysis of the vendors involved
in the various parts of 5G infrastructure – phones, radios, and
chipsets.
The report includes a discussion of the recent purchase
by Apple of Intel 5G assets, and the recent Department of Justice
approval of the T-Mobile/Sprint merger. Included is the analysis of the
implications of 5G deployment of each of these current legal events.
The
report presents, in detail, IoT, and Autonomous Vehicles as two
possible use cases often mentioned for 5G. This report also examines the
possibility of much higher levels of competition for high-speed
Internet (and other fixed services) enabled thru 5G fixed wireless. The
final main section of the report deals with specific forecasts for 5G in
the US and the impact of those forecasts on overall network
requirements.

